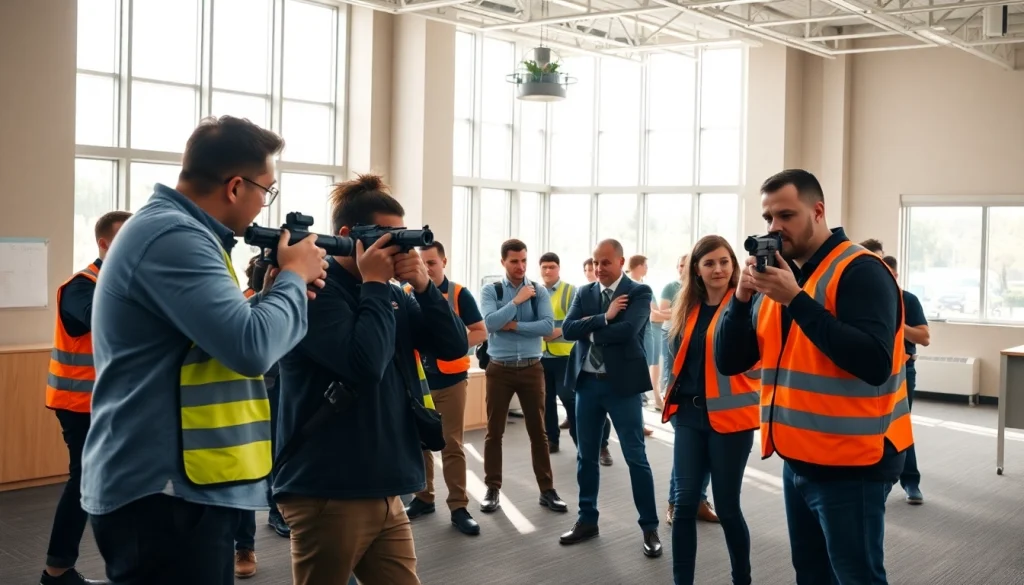
Understanding the Importance of Active Shooter Training
In an increasingly unpredictable world, the significance of active shooter training cannot be overstated. This specialized training equips individuals and organizations with the skills and knowledge to respond effectively in emergency situations involving firearms. As the frequency of active shooter incidents continues to rise, the need for comprehensive training programs has become a critical consideration for workplaces, schools, and public spaces.
Defining Active Shooter Training and Its Objectives
Active shooter training is designed to prepare individuals for the unique challenges posed by an armed assailant in a confined space. The primary objective of this training is to instill a sense of awareness, improve preparedness, and enhance response tactics. Participants learn to assess their surroundings, recognize warning signs, and develop decision-making skills that can save lives during a crisis. Key aspects of the training focus on:
- Situational awareness: Understanding how to identify potential threats.
- Emergency response protocols: Learning the steps to take during an active shooter event.
- Crisis communication: Effectively conveying information to emergency services and others.
- Escape techniques: Identifying safe exit routes and methods for evacuation.
Historical Context: Why Active Shooter Training Matters
The history of active shooter incidents has shaped the necessity for training programs. Notable events in schools, workplaces, and public spaces have highlighted the devastating impact an active shooter can have on communities. These incidents have prompted organizations and institutions to adopt proactive measures through training, emphasizing prevention and preparedness. The tragic events in recent decades have spurred legislative action, leading to the development of safety protocols and educational resources aimed at reducing risks and ensuring readiness.
Legal and Ethical Considerations for Active Shooter Training
Active shooter training encompasses various legal and ethical dimensions. Organizations must navigate liability concerns, ensuring that their training programs comply with local regulations and industry standards. Additionally, ethical considerations arise when addressing the psychological readiness of participants. Training should be conducted sensitively, acknowledging the potential for trauma while fostering a culture of safety and security. Understanding the legal implications helps institutions implement effective training without compromising their obligations to provide a safe environment.
Key Components of Effective Active Shooter Training
Core Skills and Techniques in Active Shooter Training
Effective active shooter training consists of several core skills and techniques that empower individuals to respond decisively in threatening situations. Among these skills are:
- Situational Response: Training on how to assess threats and act accordingly.
- Communication Skills: Effective sharing of information among team members and emergency personnel.
- Improvise and Adapt: Responding to rapidly changing scenarios with flexibility and quick thinking.
Participants are often engaged in practical exercises that simulate real-life scenarios, allowing them to practice these skills in a controlled environment. This hands-on approach reinforces learning and builds confidence.
Role of Simulations in Active Shooter Training
Simulations play a critical role in preparing individuals for an active shooter event. By creating realistic scenarios, training programs can simulate various environments and contexts, enabling participants to apply their knowledge in practical, high-stress situations. Simulations are designed to:
- Enhance decision-making under pressure.
- Teach team dynamics and collaboration during a crisis.
- Foster leadership and assertiveness in chaotic environments.
The use of role-playing and scenario-based training enables participants to practice their responses in a safe space. Regularly participating in such drills not only strengthens skills but also lowers anxiety levels during a real incident.
Tailoring Training Programs to Specific Environments
No two settings are alike, and effective active shooter training must reflect the specific nuances of each environment. Factors to consider include:
- Building layout and access points.
- Nature of the workforce or population served.
- Existing security measures and protocols.
- Local resources and response times from law enforcement.
By customizing training to cater to these elements, organizations can ensure that participants understand their unique situation and develop appropriate strategies for their environment.
Best Practices for Implementing Active Shooter Training
Creating a Comprehensive Training Curriculum
Developing a comprehensive training curriculum is essential for effective active shooter training. A well-structured program should include:
- A detailed introduction to the topic and overview of the course.
- Incorporation of educational and practical elements.
- Opportunities for participants to engage in discussions and share insights.
- A systematic approach to building skills progressively.
Involving experienced trainers and subject matter experts in the curriculum design process ensures the content is both relevant and credible. Regular reviews and updates to the curriculum can help maintain its effectiveness in an evolving landscape.
Assessing Participant Readiness and Engagement
To maximize the impact of training, it is crucial to assess participant readiness and engagement continually. Organizations should implement various assessment techniques, such as:
- Pre- and post-training evaluations to identify knowledge gains.
- Interactive quizzes and exercises to test retention of information.
- Observation of participant engagement during simulations.
These assessments not only gauge effectiveness but also highlight areas that may require further emphasis or refinement.
Feedback Mechanisms for Continuous Improvement
Establishing a feedback loop is vital to ensuring continuous improvement of active shooter training programs. Participants should have the opportunity to provide feedback on their experiences and training effectiveness. Effective strategies include:
- Anonymous surveys to gather honest opinions.
- Exit interviews with participants to collect insights after each session.
- Regular review sessions among staff and trainers to evaluate feedback collectively.
Implementing changes based on this feedback can help evolve the training and address any gaps in knowledge or skills required for effective crisis response.
Challenges and Solutions in Active Shooter Training
Identifying Common Barriers to Successful Training
Active shooter training faces various challenges that can hinder its effectiveness. Common barriers include:
- Lack of engagement due to perceived low relevance.
- Insufficient time allocated for comprehensive training.
- Resource constraints, including funding and personnel.
Addressing these barriers requires a commitment to prioritizing safety and ensuring that training resources—both financial and human—are allocated appropriately. Leadership buy-in is crucial to fostering a culture of preparedness.
Addressing Psychological Impacts on Participants
Active shooter training can evoke psychological responses, including anxiety and stress among participants. Addressing these psychological impacts is essential for effective training. Strategies include:
- Providing support resources for participants before and after training.
- Incorporating mental health awareness into the curriculum.
- Utilizing stress-relief techniques, such as mindfulness exercises.
Creating a supportive environment encourages participants to engage and learn confidently, reducing anxiety related to the training process.
Innovative Technologies in Active Shooter Training
Emerging technologies offer exciting possibilities for enhancing active shooter training. These innovations include:
- Virtual reality simulations that provide immersive training experiences.
- Interactive training platforms that allow for remote participation.
- Mobile applications that facilitate ongoing learning and skill development.
By integrating technology, training can become more engaging, accessible, and relevant to modern audiences. Employing these tools ensures that training is both thorough and adaptable to different learning styles.
Measuring the Success of Active Shooter Training
Defining KPIs for Effective Active Shooter Training
To evaluate the effectiveness of active shooter training programs, organizations should establish key performance indicators (KPIs) that measure success. Important KPIs may include:
- Percentage of participants who successfully complete the training.
- Improvement in response times during simulations.
- Increased awareness and understanding of safety protocols.
Collecting data related to these KPIs provides actionable insights that can formulate future training enhancements and identify areas for reinforcements.
Case Studies of Successful Active Shooter Training Programs
Examining case studies of successful active shooter training programs can provide valuable lessons and inspiration. Successful programs often share common elements, such as:
- Strong leadership support advocating for safety culture.
- Ongoing training that includes refreshers and updates.
- Community involvement, ensuring preparedness includes local law enforcement and emergency responders.
Reviewing these cases offers practical insights into best practices and strategies that have yielded positive outcomes within different environments.
Future Trends in Active Shooter Training Evaluation
As the landscape of active shooter training continues to evolve, so too does the approach to evaluation. Future trends may include:
- Increased emphasis on data analytics for assessing training efficacy.
- Integration of feedback from participants and trainers to shape training content and delivery.
- Collaboration with external experts to review training programs comprehensively.
These trends signify an ongoing commitment to improving training effectiveness while adapting to the changing nature of threats faced by organizations.